This article discusses the handling of split receipts in Dynamics GP.
More information
After you post a Purchase Order Processing receipt, you may notice that two receipt layers are created. For example, if your receipt was for a quantity of 100, you might see one receipt layer with a quantity of 99 and another with a quantity of 1. These receipt layers can be viewed in Purchase Receipts Inquiry, on the Purchase Receipts Report, or any lookup window that displays inventory receipt layers.
There are two main reasons for split receipts in Dynamics GP:
- Extended Cost Not Divisible by Quantity Received: A split receipt is created when the Extended Cost is not evenly divisible by the received quantity (Qty Shipped). This occurs because Microsoft Dynamics GP creates a separate receipt layer to ensure the total value of the item matches the Extended Cost on the purchase receipt. To view the split receipt layers, open Purchase Receipts Inquiry by navigating to the Inquiry menu, pointing to Inventory, and then clicking Receipts.
Example: Suppose we receive 3 ‘Each’ of ‘Widget A’ for a total extended cost of $1.00. Since $1.00 cannot be evenly divided by 3, two purchase receipt layers are created with the same receipt number:
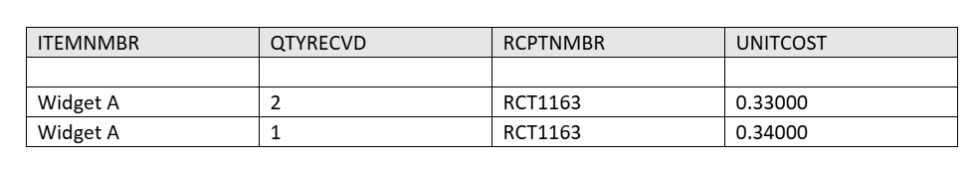 When you sell the items, the items are removed from inventory according to the valuation method of the item. Note that the 2 receipt layers represent the overall value of the receipt.
When you sell the items, the items are removed from inventory according to the valuation method of the item. Note that the 2 receipt layers represent the overall value of the receipt.
There is no adjustment that needs to be made to General Ledger to account for this.
One suggestion that may help prevent the splits of receipt layers such as this is using more decimals places for your item currency.
2. Landed Cost on Shipment/Invoice Transaction: Starting from Microsoft Dynamics GP version 10.0 SP3, when you post a shipment or shipment/invoice with a landed cost ID associated with it, a split receipt is created. This split occurs even if the Extended Cost on the receipt is evenly divisible by the quantity received. This precautionary split is necessary because when the landed cost is invoiced, it may not divide equally among the quantity received. Splitting the receipt at the time of receiving allows for easier distribution of the landed cost between the receipt layers later if required.
