Subject
Rockton Pricing Management (RPM) is a pricing engine designed to work with an ERP system like Microsoft Dynamics GP. To calculate pricing, Dynamics GP must share specific data with RPM so the web application can calculate the price and return that price to Dynamics GP.
This article explains how data flows between Dynamics GP and RPM. It also details what data must be setup directly in the Dynamics GP and what must be setup in RPM.
More Information
Overview
RPM is a stand-alone web application that integrates with multiple ERPs. In this example, Dynamics GP is the focus. The process involves the data flowing from Dynamics GP to RPM with some data coming from RPM to return a price in Dynamics GP. When you enter a transaction in Dynamics GP, RPM calculates the price from the data on the transaction and returns a price.
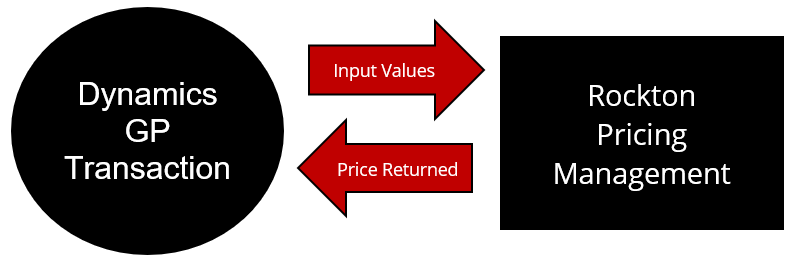
Dynamics GP to RPM
During the implementation and setup of RPM with Dynamics GP, we create triggers to ensure that when specific data is generated in Dynamics GP, it automatically triggers the creation of the same information in RPM. This ensures both programs stay in sync.
Dynamics GP creates and syncs the following to RPM:
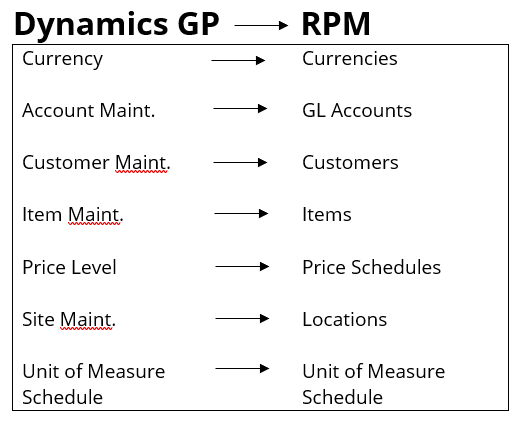
Dynamics GP always created the information sends it to RPM during the sync process. If you create the information in RPM, it does not sync back to Dynamics GP. This is also true if you edit a record. You must edit the data in Dynamics GP and then it syncs to RPM.
Deleting a record in Dynamics GP does not result in its deletion in RPM. If you no longer want the record to exist in RPM, you must delete it separately. Similarly, removing a record from RPM does not delete it from Dynamics GP.
RPM Data
After the overall setup and implementation is complete, there is data you create and and maintain within RPM. The web application uses this data when calculating an item price, and it passes it back to Dynamics GP in the form of a computed price.
Create the following data within RPM:
- Price Schedule – matches to a Price Level in Dynamics GP
- Price Calculations
- Pricing Conditions
- Attribute Maps
- Pricing Filters
- Price Books
- Catalogs
- Rounding Rules
- Customer Attributes
- Item Attributes
- Document Attributes
Note: The Attributes come from Dynamics GP but the set-up is done within RPM.
This information is used in RPM to determine the best price to compute for an item and is then passed back to Dynamics GP with the best price, based on the setup and pricing method selected.
